Self-assembled one-dimensional MnO2@zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 nanostructures for highly efficient arsenite removal†
Abstract
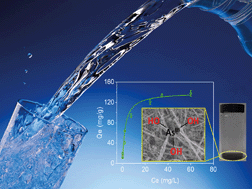
Arsenite (As(III)) is more toxic and more difficult to remove from water than arsenate (As(V)). A pre-oxidation step is therefore necessary to achieve higher removal of As(III). In this work, novel one-dimensional (1D) β-MnO2@ZIF-8 nanocomposites were successfully synthesized for the first time by a facile and rapid method to achieve concurrent oxidation and adsorptive removal of As(III). In the synthesis step, the solution medium of methanol in the reaction plays a key role in reducing the interfacial energy and promotes the integration, leading to the deposition of ZIF-8 nanocrystals on β-MnO2 nanowires. The synthesized β-MnO2@ZIF-8 exhibited a high surface area of 883 m2 g−1. Batch experimental results showed that the as-obtained β-MnO2@ZIF-8 nanocomposites could oxidize As(III) to As(V), exhibiting an improved adsorptive removal of arsenite compared to the ZIF-8 bulk. The kinetic and isotherm data of As(III) adsorption on β-MnO2@ZIF-8 nanocomposites were well fitted by pseudo-second-order and Langmuir models, respectively. The maximal adsorption capacity of As(III) was 140.27 mg g−1 at room temperature. Meanwhile, the unique 1D nanostructure of β-MnO2@ZIF-8 prevented ZIF-8 agglomeration in the aqueous solution. Moreover, the β-MnO2@ZIF-8 nanowires showed excellent settleability by gravity alone and strong mechanical stability.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...