Computer calculations across time and length scales in photovoltaic solar cells
Abstract
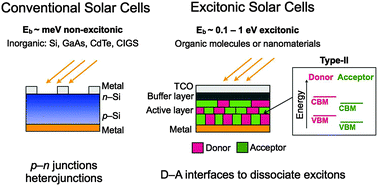
Photovoltaic (PV) solar cells convert solar energy to electricity through a cascade of microscopic processes spanning over 10 order of magnitudes of time and length. PV conversion involves a complex interplay of photons, charge carriers, and excited states. Processes following light absorption include generation of charge carriers or excitons, exciton dissociation over nanometer lengths and subpicosecond times, and carrier transport over ns–ms times and nm–mm lengths. Computer calculations have become an indispensable tool to understand and engineer solar cells across length and time scales. In this article, we examine the microscopic processes underlying PV conversion and review state-of-the-art computational methods to study PV solar cells. Recent developments and future research challenges are outlined.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...