Pyrithione-based ruthenium complexes as inhibitors of aldo–keto reductase 1C enzymes and anticancer agents†
Abstract
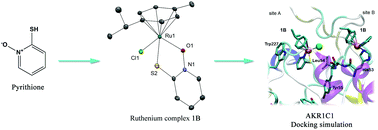
Four ruthenium complexes of clinically used zinc ionophore pyrithione and its oxygen analog 2-hydroxypyridine N-oxide were prepared and evaluated as inhibitors of enzymes of the aldo–keto reductase subfamily 1C (AKR1C). A kinetic study assisted with docking simulations showed a mixed type of inhibition consisting of a fast reversible and a slow irreversible step in the case of both organometallic compounds 1A and 1B. Both compounds also showed a remarkable selectivity towards AKR1C1 and AKR1C3 which are targets for breast cancer drug design. The organoruthenium complex of ligand pyrithione as well as pyrithione itself also displayed toxicity on the hormone-dependent MCF-7 breast cancer cell line with EC50 values in the low micromolar range.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...