Electrolysis of trichloromethylated organic compounds under aerobic conditions catalyzed by the B12 model complex for ester and amide formation†
Abstract
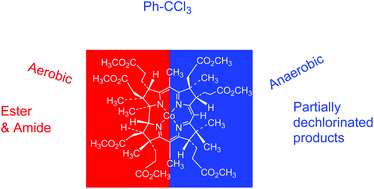
The electrolysis of benzotrichloride at −0.9 V vs. Ag/AgCl in the presence of the B12 model complex, heptamethyl cobyrinate perchlorate, in ethanol under aerobic conditions using an undivided cell equipped with a platinum mesh cathode and a zinc plate anode produced ethylbenzoate in 56% yield with 92% selectivity. The corresponding esters were obtained when the electrolysis was carried out in various alcohols such as methanol, n-propanol, and i-propanol. Benzoyl chloride was detected by GC-MS during the electrolysis as an intermediate for the ester formation. When the electrolysis was carried out under anaerobic conditions, partially dechlorinated products, 1,1,2,2-tetrachloro-1,2-diphenylethane and 1,2-dichlorostilibenes (E and Z forms), were obtained instead of an ester. ESR spin-trapping experiments using 5,5,-dimethylpyrroline N-oxide (DMPO) revealed that the corresponding oxygen-centered radical and carbon-centered radical were steadily generated during the electrolyses under aerobic and anaerobic conditions, respectively. Applications of the aerobic electrolysis to various organic halides, such as substituted benzotrichlorides, are described. Furthermore, the formation of amides with moderate yields by the aerobic electrolysis of benzotrichloride catalyzed by the B12 model complex in the presence of amines in acetonitrile is reported.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...