One-pot synthesis of polyamines improved magnetism and fluorescence Fe3O4–carbon dots hybrid NPs for dual modal imaging†
Abstract
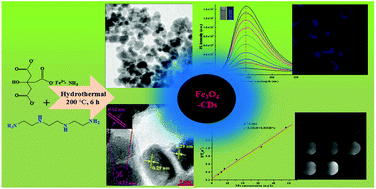
A one-step hydrothermal method was developed to fabricate Fe3O4–carbon dots (Fe3O4–CDs) magnetic–fluorescent hybrid nanoparticles (NPs). Ferric ammonium citrate (FAC) was used as a cheap and nontoxic iron precursor and as the carbon source. Moreover, triethylenetetramine (TETA) was used to improve the adhesive strength of CDs on Fe3O4 and the fluorescence intensity of CDs. The prepared water-soluble hybrid NPs not only exhibit excellent superparamagnetic properties (Ms = 56.8 emu g−1), but also demonstrate excitation-independent photoluminescence for down-conversion and up-conversion at 445 nm. Moreover, the prepared water-soluble Fe3O4–CDs hybrid NPs have a dual modal imaging ability for both magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and fluorescence imaging.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...