Antitumor and biological investigation of doubly cyclometalated ruthenium(ii) organometallics derived from benzimidazolyl derivatives†
Abstract
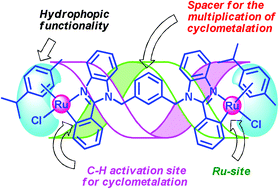
In this study, we report the synthesis, anticancer and biological properties of three doubly cyclometalated phenylbenzimidazole derived ruthenium(II) organometallics (1–3) and their corresponding three organic ligands. The structures of 1–3 were fully characterized by various analytical techniques, and the meso stereoisomer of the doubly cyclometalated ruthenacycle 3 was unambiguously confirmed by single crystal X-ray diffraction. The anticancer effects of the newly synthesized compounds were tested against selected human cancer cell lines AGS (gastric carcinoma), SK-hep-1 (hepatocellular carcinoma), and HCT-15 (colorectal carcinoma). The growth inhibitory effects of ruthenacycles 1–3 on cancer cells were found to be considerably more effective against the abovementioned cancer cells than the reference drug oxaliplatin. Compound 2 exhibited a more specific effect on the AGS cells. Gene-fishing and ELISA array were performed to analyze the target genes and cytokine secretion by 2. As a result, a significant reduction was observed in RPS21 by 2. Moreover, 2 increased the secretion of cytokines such as IFNγ in macrophages and reduced the release of cytokines such as rantes and IGF-1. These results show that 2 could be a very good anticancer drug through the regulation of the RPS21 gene and cytokines.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...