Competitive pathways of methane activation on Zn2+-modified ZSM-5 zeolite: H/D hydrogen exchange with Brønsted acid sites versus dissociative adsorption to form Zn-methyl species
Abstract
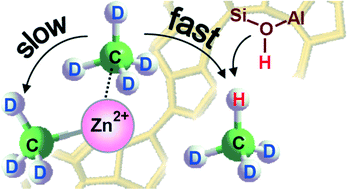
To clarify the pathways of methane activation on Zn-modified high-silica zeolites, the kinetics of both dissociative adsorption of the alkane C–H bond to form Zn-methyl species and H/D hydrogen exchange between the alkane and Brønsted acid sites (BAS) have been analyzed for Zn2+/H-ZSM-5 containing exclusively Zn2+ cations (no ZnO species in the zeolite) and BAS. Analysis of the kinetics was performed by 1H MAS NMR spectroscopy in situ at 410–540 K. In spite of the activation barrier for H/D hydrogen exchange (68 kJ mol−1) being larger than that for Zn-methyl formation (46 kJ mol−1), the rate of H/D hydrogen exchange has been found to be one order of magnitude higher than the rate of the formation of Zn-methyl species within the studied temperature range. This implies that Zn-methyl species cannot be involved in the reaction of H/D hydrogen exchange as the intermediate responsible for facilitation of this reaction due to the presence of Zn2+ cations in the zeolite (J. Catal., 2008, 253, 11). A new mechanism has been suggested for C–H bond activation in methane on the zeolite modified with Zn2+ cations. It includes first the formation of a transient molecular complex of methane with Zn2+ cations. The complex either is further involved in the reaction of H/D hydrogen exchange or evolves toward the formation of Zn-methyl species and BAS.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...