A Pd–bisphosphine complex and organic functionalities immobilized on the same SiO2 surface: detailed characterization and its use as an efficient catalyst for allylation†
Abstract
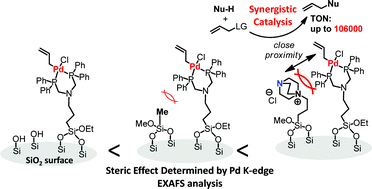
A Pd–bisphosphine complex and several organic functionalities were immobilized on the same SiO2 surface. The samples thus prepared were characterized by solid-state NMR, XPS, and XAFS. Based on the curve-fitting analysis of Pd K-edge EXAFS spectra, both the local environment of the immobilized Pd complexes and the interactions with the co-immobilized organic functions were discussed. The SiO2-supported Pd–bisphosphine complex and DABCO exhibited excellent catalytic performance for the allylation of various nucleophiles: a TON of up to 106 000 was obtained. Both the catalyst activation pathway and the reaction mechanism were also discussed on the basis of the structure of the used catalyst samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...