Design of iron catalysts supported on carbon–silica composites with enhanced catalytic performance in high-temperature Fischer–Tropsch synthesis†
Abstract
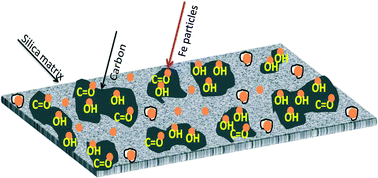
A series of iron catalysts supported over carbon–silica composite materials were prepared using fructose via a mild hydrothermal approach. The catalysts exhibited very high surface areas (∼300 m2 g−1) and good iron dispersion. Different from conventional silica-supported catalysts, no interaction between iron and silica was observed. Iron moieties were conveniently immobilized onto carbon dispersed over the silica support. A combination of characterization techniques confirmed the presence of iron in the lower oxidation state after calcination in the carbon–silica composites compared to the silica-supported catalysts. The in situ magnetic measurement and in situ XRD were indicative of iron carbide formation during CO activation. Higher carbon content in the carbon–silica composite catalysts favoured the coverage of a higher fraction of the catalyst surface by carbon species and direct interaction of a higher concentration of iron carbide species with the carbon support. The Fischer–Tropsch tests showed enhanced performance of the iron catalysts supported on the carbon–silica composite materials compared to the silica- and pure carbon-supported counterparts.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...