Substituting effect of Ce3+ on the AlPO-11 molecular sieve†
Abstract
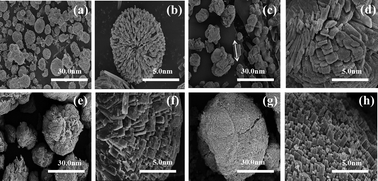
Substituted AlPO-11 molecular sieve with Ce3+ was first prepared. The substitution was verified by characterization techniques and density functional theory. The results showed that both Al3+ and P5+ sites could be substituted. Cerium–oxygen tetrahedron was formed when Al3+ sites were replaced via isomorphous substitution. As for substituting the P5+ sites, Ce3+ coordinated with two or three oxygen atoms to form surface defects. Brønsted and Lewis acid sites appeared from the charge compensation and structure defects, respectively. The defective surface with higher interface energy resulted in particle aggregation and oriented growth. CeAPO-11 possesses a superior hydrothermal stability, which enables its application in a steam atmosphere with severely high temperatures. It was added as the bi-functional promoter (isomerization and dehydrogenation) to a fluid catalytic cracking catalyst. The results showed that CeAPO-11 increased the reaction conversion and the selectivity of aromatics and cycloparaffins.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...