Horseradish peroxidase (HRP): a tool for catalyzing the formation of novel bicoumarins†
Abstract
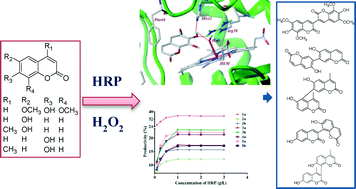
Horseradish peroxidase (HRP) was used to effectively catalyze the dimerization of coumarins. On the basis of screening and preparative transformation, the catalytic ability of HRP to dimerize various coumarins was investigated. Coumarins that only had one substituted phenolic hydroxyl group could be selectively transformed into novel bicoumarins, while coumarins that had two or more hydroxyls could be transformed into multiple bicoumarins. Eight bicoumarins were obtained and identified by spectroscopic analysis. Among them, bicoumarins 1b, 2a, 2b, 3a and 3b are reported here for the first time. The interactions between the different types of coumarins and HRP were also investigated by in silico docking analysis. Using the transformed products as standard substances, kinetic analyses of the catalytic reactions were carried out. The optimized reaction conditions for the dimerization of coumarins catalyzed by HRP were 1 g L−1 HRP, 0.66 M H2O2, pH 3, 25 °C, and 15 min of incubation time. The yields of the bicoumarins ranged from 10 to 40%, especially for bicoumarin 1a, which was obtained in approximately 35% yield. In an in vitro bioassay, several novel bicoumarins displayed potential α-glucosidase inhibitory activities, which can be further used to develop antidiabetic agents.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...