The effect of surface oxygenated groups of carbon nanotubes on liquid phase catalytic oxidation of cumene
Abstract
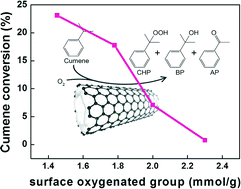
It is of particular interest to reveal the influence of surface oxygenated groups and surface defects of carbon catalysts on liquid phase oxidation reactions. Herein, surface oxygenated groups and defects were introduced on the surface of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) using a gas-phase oxidation method with O2 and a liquid-phase oxidation method with concentrated HNO3. The results strongly confirm that the surface oxygenated groups on CNTs have a negative effect on catalytic activity for cumene oxidation. To the best of our knowledge, for the first time, we have distinguished experimentally that the factor responsible for the decrease in catalytic activity of the oxidized CNTs for the liquid phase aerobic oxidation reaction is the surface oxygenated groups instead of the surface defects. Meanwhile, the mechanism that drives the decrease in catalytic activity of the oxidized CNTs has also been revealed. It has been proven that the oxidized CNTs serve as free radical quenchers, capturing the free radical intermediates of the reaction and inhibiting the free radical chain transfer, thereby reducing the catalytic activity of the free radical reaction in the liquid phase. This study gains a new insight into the effect of surface structures on carbon-catalyzed liquid phase oxidation, and further pushes forward the research on carbon catalysis.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...