Phosphorus-doped ordered mesoporous carbons embedded with Pd/Fe bimetal nanoparticles for the dechlorination of 2,4-dichlorophenol†
Abstract
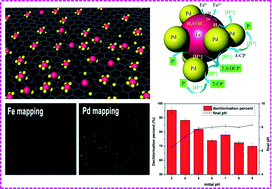
Palladium/iron (Pd/Fe) bimetallic nanoparticles were embedded within phosphorus-doped ordered mesoporous carbons (Pd/NZVI@P) with high dechlorination activity for 2,4-dichlorophenol (2,4-DCP). The Pd/Fe bimetal nanoparticles of about 15 nm diameter embedded in phosphorus-doped ordered mesoporous carbons (P-OMCs) were homogeneously distributed. The high dechlorination activity was mainly attributed to the homogeneous distribution of Pd/Fe bimetal nanoparticles, which were characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and scanning electron microscopy/energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry (SEM/EDS) with image mapping. Dechlorination kinetics indicated that the dechlorination rates of 2,4-DCP increased with the increasing of Pd content. The use of P-OMCs as supporting materials to embed enough Pd/Fe bimetal nanoparticles kept the nanoparticles highly active and stable. Besides, solution pH had a significant effect on the dechlorination of 2,4-DCP and the passivation of the Pd/NZVI@P samples. The effects of the number and position of chlorine atoms for different chlorophenols (CPs) on the dechlorination activity were also revealed; the result indicated that the dechlorination of CPs by catalytic reduction preferentially begins from the para-position of the ring, and more chlorine atoms of CPs are favorable for the occurrence of the dechlorination reaction. This study demonstrated that P-OMC is a promising supporting material for the preparation of some effective composite metals for the catalytic dechlorination of CPs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...