Correlating the chemical composition and size of various metal oxide substrates with the catalytic activity and stability of as-deposited Pt nanoparticles for the methanol oxidation reaction†
Abstract
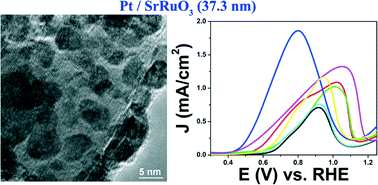
The performance of electrode materials in conventional direct alcohol fuel cells (DAFC) is constrained by (i) the low activity of the catalyst materials relative to their overall cost, (ii) the poisoning of the active sites due to the presence of partially oxidized carbon species (such as but not limited to CO, formate, and acetate) produced during small molecule oxidation, and (iii) the lack of catalytic stability and durability on the underlying commercial carbon support. Therefore, as a viable alternative, we have synthesized various metal oxide and perovskite materials of different sizes and chemical compositions as supports for Pt nanoparticles (NPs). Our results including unique mechanistic studies demonstrate that the SrRuO3 substrate with immobilized Pt NPs at its surface evinces the best methanol oxidation performance as compared with all of the other substrate materials tested herein, including commercial carbon itself. Additionally, data from electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) confirmed the presence of electron transfer from bound Pt NPs to surface Ru species within the SrRuO3 substrate itself, thereby suggesting that favorable metal support interactions are responsible for the increased methanol oxidation reaction (MOR) activity of Pt species with respect to the underlying SrRuO3 composite catalyst material.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...