pH-regulated surface properties and pH-reversible micelle transition of a zwitterionic gemini surfactant in aqueous solution†
Abstract
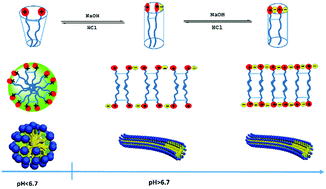
A zwitterionic gemini surfactant, called 2,2′-(1,4-phenylenebis(oxy))bis(N,N-dimethyl)-N-carboxyethyl-N-(alkylamide propyl) ammonium chloride (C14–B–C14), was synthesized successfully. The surfactant molecule exhibits various states at different pH values due to the two pH-sensitive carboxylate groups in the molecule. The surface activity and aggregate behaviors of C14–B–C14 in the aqueous solution were investigated under different pH conditions. The surface activities of the surfactant decrease with the increase in pH due to higher hydrophilic properties under basic conditions. The aggregate behaviours were also studied in acidic, near neutral and alkaline solutions, respectively. When the pH values of the solutions increased from acidic conditions to near neutral conditions (6.80), the samples immediately transformed from water-like solutions to viscoelastic fluids and remained gel-like under basic conditions. The changes in the appearance of the solution were due to the transition of the micelle structure from spherical to worm-like. Furthermore, this transition was reversible and repeated for at least 4 cycles. Finally, a reasonable mechanism of the appearance and transition of micelles was proposed based on the molecular states, viscoelastic properties and micelle structures.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...