Photoluminescence study of time- and spatial-dependent light induced trap de-activation in CH3NH3PbI3 perovskite films†
Abstract
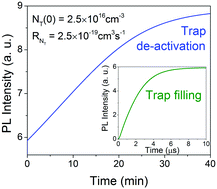
Organometal halide perovskite-based solar cells have rapidly achieved high efficiency in recent years. However, many fundamental recombination mechanisms underlying the excellent performance are still not well understood. Here we apply confocal photoluminescence microscopy to investigate the time and spatial characteristics of light-induced trap de-activation in CH3NH3PbI3 perovskite films. Trap de-activation is characterized by a dramatic increase in PL emission during continuous laser illumination accompanied by a lateral expansion of the PL enhancement far beyond the laser spot. These observations are attributed to an oxygen-assisted trap de-activation process associated with carrier diffusion. To model this effect, we add a trap de-activation term to the standard semiconductor carrier recombination and diffusion models. With this approach we are able to reproduce the observed temporal and spatial dependence of laser induced PL enhancement using realistic physical parameters. Furthermore, we experimentally investigate the role of trap diffusion in this process, and demonstrate that the trap de-activation is not permanent, with the traps appearing again once the illumination is turned off. This study provides new insights into recombination and trap dynamics in perovskite films that could offer a better understanding of perovskite solar cell performance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...