Synthesis of eucalyptus/tea tree oil absorbed biphasic calcium phosphate–PVDF polymer nanocomposite films: a surface active antimicrobial system for biomedical application†
Abstract
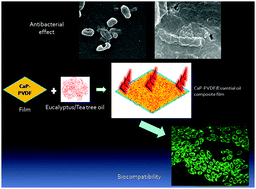
A biocompatible poly(vinylidene) difluoride (PVDF) based film has been prepared by in situ precipitation of calcium phosphate precursors. Such films were surface absorbed with two essential oils namely eucalyptus and tea tree oil. Physico-chemical characterization of the composite film revealed excellent stability of the film with 10% loading of oils in the PVDF matrix. XRD, FTIR and FESEM measurements confirmed the presence of hydroxyapatite and octacalcium phosphate in the PVDF matrix which showed predominantly β phase. Strong bactericidal activity was observed with very low minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) values on both E. coli and S. aureus. The composite films also resisted biofilm formation as observed by FESEM. The release of essential oils from the film showed an initial burst followed by a very slow release over a period of 24 hours. Antibacterial action of the film was found to be primarily due to the action of essential oils which resulted in leakage of vital fluids from the microorganisms. Both necrotic and apoptotic morphologies were observed in bacterial cells. Biocompatibility studies with the composite films showed negligible cytotoxicity to mouse mesenchymal and myoblast cells at MBC concentration.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...