Melting of gelatin gels confined to silica nanopores
Abstract
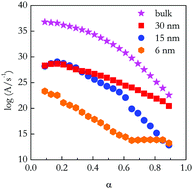
Nanoconfinement is a way to create materials whose properties differ from the bulk. For the first time, this research explores the effect of nanoconfinement on the thermodynamics and kinetics of gel melting. Differential scanning calorimetry has been employed to study gelatin gels prepared inside 4, 6, 15, and 30 nm pores of a silica matrix. It has been found that with decreasing the pore size the heat of melting decreases from 3.5 J g−1 in bulk to 0.6 J g−1 in 6 nm pores, which is linked to a decrease in crosslinks formed via hydrogen bonding. Despite decreases in crosslink formation, the melting temperature for gels confined to 6 nm pores increased nearly 10 °C compared to bulk gel. In 4 nm pores, no gel melting was observed. Isoconversional kinetic analysis of the melting data has revealed that the increase in thermal stability is associated with a decrease in the pre-exponential factor that occurs upon nanoconfinement. The origins of the effect have been linked to diminished molecular mobility of the gelatin chains confined inside the nanopores, which leads to enhanced restoration of broken crosslinks.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...