Redox chemistry of a binary transition metal oxide (AB2O4): a study of the Cu2+/Cu0 and Fe3+/Fe0 interconversions observed upon lithiation in a CuFe2O4 battery using X-ray absorption spectroscopy†
Abstract
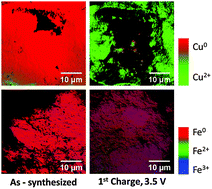
Copper ferrite, CuFe2O4, is a promising candidate for application as a high energy electrode material in lithium based batteries. Mechanistic insight on the electrochemical reduction and oxidation processes was gained through the first X-ray absorption spectroscopic study of lithiation and delithiation of CuFe2O4. A phase pure tetragonal CuFe2O4 material was prepared and characterized using laboratory and synchrotron X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, and transmission electron microscopy. Ex situ X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) measurements were used to study the battery redox processes at the Fe and Cu K-edges, using X-ray absorption near-edge structure (XANES), extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS), and transmission X-ray microscopy (TXM) spectroscopies. EXAFS analysis showed upon discharge, an initial conversion of 50% of the copper(II) to copper metal positioned outside of the spinel structure, followed by a migration of tetrahedral iron(III) cations to octahedral positions previously occupied by copper(II). Upon charging to 3.5 V, the copper metal remained in the metallic state, while iron metal oxidation to iron(III) was achieved. The results provide new mechanistic insight regarding the evolution of the local coordination environments at the iron and copper centers upon discharging and charging.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...