Surface modification of battery electrodes via electroless deposition with improved performance for Na-ion batteries†
Abstract
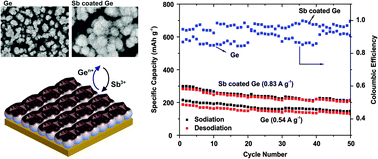
Sodium-ion batteries (SIBs) are emerging as potential stationary energy storage devices due to the abundance and low cost of sodium. A simple and energy efficient strategy to develop electrodes for SIBs with a high charge/discharge rate is highly desirable. Here we demonstrate that by surface modification of Ge, using electroless deposition in SbCl3/ionic liquids, the stability and performance of the anode can be improved. This is due to the formation of GexSb1−x at the surface leading to better diffusion of Na, and the formation of a stable twin organic and inorganic SEI which protects the electrode. By judicious control of the surface modification, an improvement in the capacity to between 50% and 300% has been achieved at high current densities (0.83–8.4 A g−1) in an ionic liquid electrolyte NaFSI-[Py1,4]FSI. The results clearly demonstrate that an electroless deposition based surface modification strategy in ionic liquids offers exciting opportunities in developing superior energy storage devices.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...