Adsorption isotherms for hydrogen chloride (HCl) on ice surfaces between 190 and 220 K
Abstract
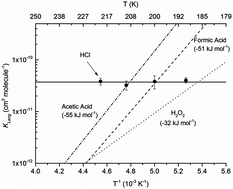
The interaction of hydrogen chloride (HCl) with ice surfaces at temperatures between 190 and 220 K was investigated using a coated-wall flow-tube connected to a chemical ionization mass spectrometer. Equilibrium surface coverages of HCl were determined at gas phase concentrations as low as 2 × 109 molecules cm−3 (∼4 × 10−8 Torr at 200 K) to derive Langmuir adsorption isotherms. The data are described by a temperature independent partition coefficient: KLang = (3.7 ± 0.2) × 10−11 cm3 molecule−1 with a saturation surface coverage Nmax = (2.0 ± 0.2) × 1014 molecules cm−2. The lack of a systematic dependence of KLang on temperature contrasts the behaviour of numerous trace gases which adsorb onto ice via hydrogen bonding and is most likely related to the ionization of HCl at the surface. The results are compared to previous laboratory studies, and the equilibrium partitioning of HCl to ice surfaces under conditions relevant to the atmosphere is evaluated.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...