Thermal decomposition of sodium amide, NaNH2, and sodium amide hydroxide composites, NaNH2–NaOH†
Abstract
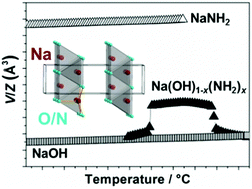
Sodium amide, NaNH2, has recently been shown to be a useful catalyst to decompose NH3 into H2 and N2, however, sodium hydroxide is omnipresent and commercially available NaNH2 usually contains impurities of NaOH (<2%). The thermal decomposition of NaNH2 and NaNH2–NaOH composites is systematically investigated and discussed. NaNH2 is partially dissolved in NaOH at T > 100 °C, forming a non-stoichiometric solid solution of Na(OH)1−x(NH2)x (0 < x < ∼0.30), which crystallizes in an orthorhombic unit cell with the space group P212121 determined by synchrotron powder X-ray diffraction. The composite xNaNH2–(1 − x)NaOH (∼0.70 < x < 0.72) shows a lowered melting point, ∼160 °C, compared to 200 and 318 °C for neat NaNH2 and NaOH, respectively. We report that 0.36 mol of NH3 per mol of NaNH2 is released below 400 °C during heating in an argon atmosphere, initiated at its melting point, T = 200 °C, possibly due to the formation of the mixed sodium amide imide solid solution. Furthermore, NaOH reacts with NaNH2 at elevated temperatures and provides the release of additional NH3.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...