Halogenated earth abundant metalloporphyrins as photostable sensitizers for visible-light-driven water oxidation in a neutral phosphate buffer solution†
Abstract
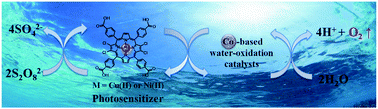
Very photostable tetrachloro-metalloporphyrins were developed as sensitizers for visible-light-driven water oxidation coupled to cobalt based water-oxidation catalysts in concentrated (0.1 M) phosphate buffer solution. Potassium persulfate (K2S2O8) acts as a sacrificial electron acceptor to oxidize the metalloporphyrin photosensitizers in their excited states. The radical cations thus produced drive the cobalt based water-oxidation catalysts: Co4O4-cubane and Co(NO3)2 as pre-catalyst for cobalt-oxide (CoOx) nanoparticles. Two different metalloporphyrins (Cu(II) and Ni(II)) both showed very high photostability in the photocatalytic reaction, as compared to non-halogenated analogues. This indicates that photostability primarily depends on the substitution of the porphyrin macrocycle, not on the central metal. Furthermore, our molecular design strategy not only positively increases the electrochemical potential by 120–140 mV but also extends the absorption spectrum up to ∼600 nm. As a result, the solar photon capturing abilities of halogenated metalloporphyrins (Cu(II) and Ni(II)) are comparable to that of the natural photosynthetic pigment, chlorophyll a. We successfully demonstrate long-term (>3 h) visible-light-driven water oxidation using our molecular system based on earth-abundant (first-row transition) metals in concentrated phosphate buffer solution.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...