Acyclic forms of aldohexoses and ketohexoses in aqueous and DMSO solutions: conformational features studied using molecular dynamics simulations†
Abstract
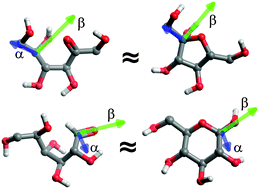
The molecular properties of aldohexoses and ketohexoses are usually studied in the context of their cyclic, furanose or pyranose structures which is due to the abundance of related tautomeric forms in aqueous solution. We studied the conformational features of a complete series of D-aldohexoses (D-allose, D-altrose, D-glucose, D-mannose, D-gulose, D-idose, D-galactose and D-talose) and D-ketohexoses (D-psicose, D-fructose, D-sorbose and D-tagatose) as well as of L-psicose by using microsecond-timescale molecular dynamics in explicit water and DMSO with the use of enhanced sampling methods. In each of the studied cases the preferred conformation corresponded to an extended chain structure; the less populated conformers included the quasi-cyclic structures, close to furanose rings and common for both aldo- and ketohexoses. The orientational preferences of the aldehyde or ketone groups are correlated with the relative populations of anomers characteristic of cyclic aldo- and ketohexoses, respectively, thus indicating that basic features of anomeric equilibria are preserved even if hexose molecules are not in their cyclic forms. No analogous relationship is observed in the case of other structural characteristics, such as the preferences of acyclic molecules to form either the furanose-or pyranose-like structures or maintaining the chair-like geometry of pseudo-pyranose rings.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...