Rare-earth-free red-emitting K2Ge4O9:Mn4+ phosphor excited by blue light for warm white LEDs†
Abstract
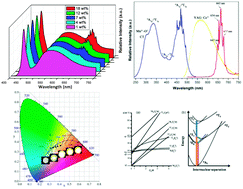
A series of novel K2Ge4O9:Mn4+ phosphors with red emission under blue light excitation have been synthesized successfully by traditional high-temperature solid-state reaction. The structure of K2Ge4O9 has been investigated by high-resolution transmission electron microscopy, scanning electron microscopy and X-ray powder diffraction with Rietveld refinement. The PL properties have been investigated by measuring diffuse reflection spectra, emission spectra, excitation spectra, decay curves and temperature-dependent spectra. The KGO:0.1% Mn4+ phosphor can emit red light peaking at 663 nm under UV or blue light excitation. The critical quenching concentration of Mn4+ was about 0.1 mol%. The concentration quenching mechanism could be a d–d interaction for the Mn4+ center. The CIE chromaticity coordinates and FWHM are (0.702, 0.296) and 20 nm, which demonstrated that the K2Ge4O9:Mn4+ has a high color purity. By tuning the weight ratio of yellow and red phosphors, the fabricated white LEDs, using a 455 nm InGaN blue chip combined with a blend of the yellow phosphor YAG:Ce3+ and the red-emitting KGO:Mn4+ phosphor driven by a 40 mA current, can get white light with chromaticity coordinates (0.405, 0.356) and CCT 3119 K. These results indicated that K2Ge4O9:Mn4+ is a potential red phosphor to match blue LED chips to get warm white light.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...