Identifying the redox activity of cation-disordered Li–Fe–V–Ti oxide cathodes for Li-ion batteries
Abstract
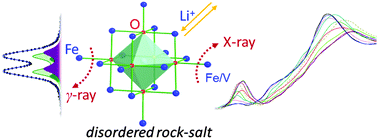
Cation-disordered oxides have recently shown promising properties on the way to explore high-performance intercalation cathode materials for rechargeable Li-ion batteries. Here, stoichiometric cation-disordered Li2FeVyTi1−yO4 (y = 0, 0.2, 0.5) nanoparticles are studied. The substitution of V for Ti in Li2FeVyTi1−yO4 increases the content of active transition metals (Fe and V) and accordingly the amount of Li+ (about (1 + y)Li+ capacity per formula unit) that can be reversibly intercalated. It is found that Fe3+/Fe2+ and V4+/V3+ redox couples contribute to the overall capacity performance, whereas Ti4+ remains mainly inert. There is no evidence for the presence of Fe4+ species after charging to 4.8 V, as confirmed from the ex situ57Fe Mössbauer spectroscopy and the Fe K-edge absorption spectra. The redox couple reactions for iron and vanadium are examined by performing in situ synchrotron X-ray absorption spectroscopy. During charging/discharging, the spectral evolution of the K-edges for Fe and V confirms the reversible Fe3+/Fe2+ and V4+/V3+ redox reactions during cycling between 1.5 and 4.8 V.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...