Intramolecular structure and energetics in supercooled water down to 255 K
Abstract
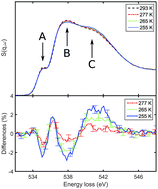
We studied the structure and energetics of supercooled water by means of X-ray Raman and Compton scattering. Under supercooled conditions down to 255 K, the oxygen K-edge measured by X-ray Raman scattering suggests an increase of tetrahedral order similar to the conventional temperature effect observed in non-supercooled water. Compton profile differences indicate contributions beyond the theoretically predicted temperature effect and provide a deeper insight into local structural changes. These contributions suggest a decrease of the electron mean kinetic energy by 3.3 ± 0.7 kJ (mol K)−1 that cannot be modeled within established water models. Our surprising results emphasize the need for water models that capture in detail the intramolecular structural changes and quantum effects to explain this complex liquid.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...