Synthesis of morphology-controlled bismutite for selective applications†
Abstract
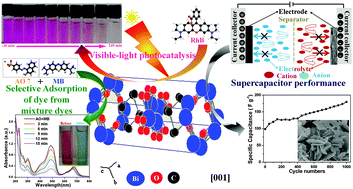
Bismutite (Bi2O2CO3) possessing diverse morphologies, namely nanosheets, nanodiscs and nanoplatelets, was synthesized by a simple controllable method using bismuth nitrate pentahydrate and urea as precursors in a water/ethylene glycol mixture. The as-synthesized samples showed unique physical and chemical properties, such as varying morphology, phase identification, chemical composition, surface area and surface potential. Bi2O2CO3 nanosheets exhibited excellent adsorption capabilities for anionic dyes (acid orange 7 and methyl orange) and high photocatalytic performance for the decolorization of cationic dyes (rhodamine B and methylene blue) under simulated solar illumination. Furthermore, the electrochemical performance of Bi2O2CO3 nanosheets showed good capacitance properties and hence could be a potential candidate for electrode materials in energy related applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...