Binding properties of pendimethalin herbicide to DNA: multispectroscopic and molecular docking approaches
Abstract
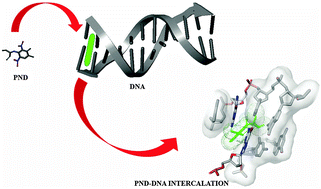
Pendimethalin (PND) is a systemic herbicide widely used on rice, cotton, peas, wheat, potatoes, fruits, nuts and other residential and non-residential crops; however, it concurrently exerts toxic effects on beneficial organisms like earthworms, aquatic invertebrates and other non-targeted animals including humans. Most likely, the genotoxicity of agrochemicals/drugs is modulated through cellular distribution of bound DNA. Therefore, the in vitro interaction of PND with calf thymus DNA (ctDNA) has been investigated using various sensitive biophysical techniques to ascertain its binding mechanism. UV-visible absorption and fluorescence spectra suggested the formation of a complex between PND and ctDNA. The binding constant of the PND–ctDNA complex was found to be around 104 M−1 using steady state fluorescence titration. The calculated positive values of enthalpy and entropy changes suggested that the binding reaction was predominantly driven by hydrophobic interactions. Competitive displacement studies using acridine orange (AO), ethidium bromide (EB) and Hoechst dye suggested intercalation of PND molecules into the double helix of ctDNA by replacing the bound AO and EB probes. An increase in the viscosity and melting temperature of ctDNA and a decrease in iodine-quenching also support the intercalative binding of PND with ctDNA. Molecular docking analysis further confirmed the specific binding mode of PND between adjacent ‘G–C’ base pairs of ctDNA.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...