Optical and morphological properties of thin films of bis-pyrenyl π-conjugated molecules†
Abstract
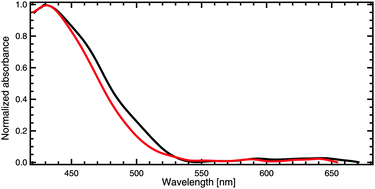
1,4-Di-n-octyloxy-2,5-bis(pyren-1-ylethenyl)benzene (bis-pyrene) has been studied by the means of surface cavity ring-down (s-CRD) spectroscopy on an amorphous BK7 glass substrate and scanning tunnelling microscopy (STM) on Au(111). Absorption spectra show a modification of the optical properties as a function of coverage, i.e. appearance of a shoulder around 505 nm followed by a saturation of the intensity of this signal observed at higher coverages. We attribute this shoulder to the change of the molecular orientation between the first and the second monolayer and thus to an interfacial effect. These results are confirmed by scanning tunnelling microscopy (STM) measurements where the bis-pyrene molecules have been deposited on Au(111) at room temperature (RT) and onto a cold substrate. Independently of the temperature in the range from 210 K to RT, the first monolayer is always highly organized. At low temperature bis-pyrene molecules constituting the second monolayer are randomly distributed, suggesting that self-organisation is kinetically hindered. Deposited at room temperature, the molecular diffusion is enhanced and the formation of an organized second layer takes place after storing the sample for 150 minutes at room temperature. A HOMO–LUMO gap of 2.85 eV has been determined by scanning tunnelling spectroscopy, which is in very good agreement with the observed optical transition at 434 nm (2.86 eV) in s-CRD spectroscopy.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...