Abstract
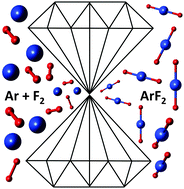
On account of the rapid development of noble gas chemistry in the past half-century both xenon and krypton compounds can now be isolated in macroscopic quantities. The same does not hold true for the next lighter group 18 element, argon, which forms only isolated molecules stable solely in low temperature matrices or supersonic jet streams. Here we present theoretical investigations into a new high-pressure reaction pathway, which enables synthesis of argon fluorides in bulk and at room temperature. Our hybrid DFT calculations (employing the HSE06 functional) indicate that above 60 GPa ArF2-containing molecular crystals can be obtained by a reaction between argon and molecular fluorine.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...