A study on the synthesis, pair distribution function and diverse properties of cobalt doped ZnS nanowires†
Abstract
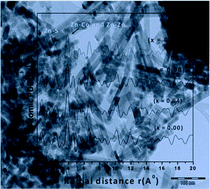
Nanowires of undoped and cobalt doped ZnS were synthesized by a hydrothermal method. The samples of pure and Co doped ZnS were characterized by ADXRD. The structural parameters were evaluated using the ADXRD data. The atomic structures of pure and Co doped ZnS nanowires have been studied using pair distribution function (PDF) analysis. It was confirmed that the samples have a hexagonal (wurtzite) structure. The interatomic distance was calculated using PDF analysis. The energy band gaps of pure and Co doped ZnS nanowires were estimated using UV-vis spectra, and a red shift was clearly observed. It was also observed that the energy band gap decreases as the Co content increases. The FTIR spectra indicate that Co is substituted in the ZnS lattice. The TEM micrographs clearly show the growth of nanowires of the synthesized samples. A vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) was used to outline the presence of magnetism in the sample. It was confirmed from the VSM that as-synthesized pure and Co doped ZnS nanoparticles exhibit weak ferromagnetism at room temperature.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...