Crystal structures and physicochemical properties of diltiazem base and its acetylsalicylate, nicotinate and l-malate salts†
Abstract
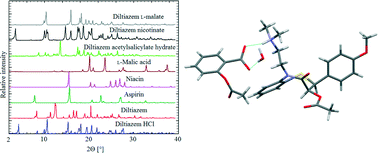
Diltiazem is a drug used as a calcium channel blocker in the treatment of cardiovascular disorders. Because of the poor aqueous solubility of the drug, its hydrochloride salt has been marketed. Due to the short elimination half-life of diltiazem, extended-release formulations were developed. In the present work, the crystal engineering approach has been employed to obtain diltiazem forms with lower water solubility by treating with carboxylic acids. Three molecular salts of diltiazem with aspirin, niacin and L-malic acid were synthesized and characterized by single crystal and powder XRD, DTA, solid state CP-MAS, NMR and UV/vis techniques. The single crystal structure determination allowed us to study the supramolecular structures and proton transfer interactions from the carboxylic acids to diltiazem in the solid state, while the NMR studies showed the interactions in solution. In the crystal, the N,N-(dimethyl)ethylamine fragment of the drug molecule interacts with the carboxylic groups of the acids to form heterosynthons. The maximum 40-fold decrease of the aqueous solubility is achieved for diltiazem acetylsalicylate hydrate in comparison with the solubility of diltiazem hydrochloride.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...