Light-controllable toxicity recovery from selenium-based amphiphiles†
Abstract
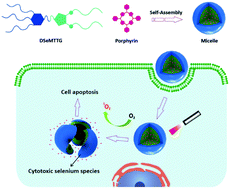
A selenium-containing anticancer compound DSeMTTG was prepared, which could be self-assembled into a unimolecular amphiphilic drug nanoassembly (UADN) with good biocompatibility. The resulting UADN was sensitive to singlet oxygen produced by encapsulated porphyrin photosensitizers. Thus, the toxicity of DSeMTTG could be retrieved after visible light irradiation, which significantly inhibited the proliferation of A549 cells without using extra chemotherapeutic drugs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...