Iron-catalyzed oxidative sp3 carbon–hydrogen bond functionalization of 3,4-dihydro-1,4-benzoxazin-2-ones†
Abstract
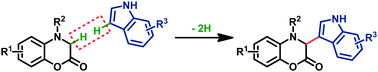
A novel and efficient iron-catalyzed sp3 carbon–hydrogen bond functionalization of benzoxazinone derivatives has been developed. For the first time, benzoxazin-2-ones were used as substrates in an oxidative dehydrogenative coupling reaction. The experiments were performed under mild reaction conditions to construct alkyl–aryl C(sp3)–C(sp2) bonds. The application of this method to the gram-scale synthesis of natural product cephalandole A has been accomplished in a 3-step sequence. A plausible one electron oxidation involved mechanism is proposed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...