Interlayer-I-doped BiOIO3 nanoplates with an optimized electronic structure for efficient visible light photocatalysis†
Abstract
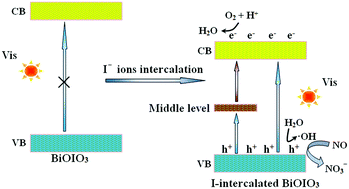
The success in the synthesis of Bi-based layered photocatalysts with high photocatalytic activities has triggered intensive studies. Herein, we prepared interlayer-I-doped BiOIO3 nanoplates by a facile method. Interestingly, it was found that I atoms were doped into the BiOIO3 interlayers instead of substituting for the lattice atoms based on theoretical and experimental results. The interbedded I atoms endowed BiOIO3 with an extended light response from the UV to the visible region by narrowing the bandgap and generating a middle level. The enhanced oxidation capability via positive-shifting the valence band position and improved carrier separation efficiency via forming charge delivery channels at the adjacent two layers can be achieved simultaneously. As expected, I-intercalated BiOIO3 with an optimized electronic structure demonstrated outstanding NO removal ability under visible light irradiation, much superior to pure BiOIO3. The present success in fabricating interlayer-I-doped BiOIO3 would open a promising route to prepare other Bi-based layered semiconductors with efficient visible-light photocatalysis.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...