Immobilization of iron oxide nanoparticles within alginate nanogels for enhanced MR imaging applications†
Abstract
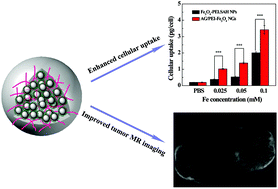
We report the design of iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticle (NP)-immobilized alginate (AG) nanogels (NGs) as a novel contrast agent for enhanced magnetic resonance (MR) imaging applications. In this study, an aqueous solution of AG activated by 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride was double emulsified to form NGs, followed by in situ cross-linking with polyethyleneimine (PEI)-coated Fe3O4 NPs (PEI-Fe3O4 NPs). The resultant Fe3O4 NP-immobilized AG NGs (AG/PEI-Fe3O4 NGs) were characterized via different techniques. Our results reveal that the hybrid NGs with a size of 186.1 ± 33.1 nm are water dispersible, colloidally stable, and cytocompatible in the given concentration range. Importantly, these NGs have a high r2 relaxivity (170.87 mM−1 s−1) due to the high loading of Fe3O4 NPs within the NGs, and can be more significantly uptaken by cancer cells when compared with carboxylated Fe3O4 NPs. The formed AG/PEI-Fe3O4 NGs are able to be used as an effective contrast agent for the MR imaging of cancer cells in vitro and the xenografted tumor model in vivo after intravenous injection. The developed AG/PEI-Fe3O4 NGs may hold great promise for use as a novel contrast agent for the enhanced MR imaging of different biological systems.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...