Multivariate optimization of PTV-GC-MS method for simultaneous determination of organometallic compounds of mercury, lead and tin
Abstract
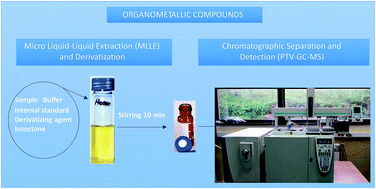
A simple, rapid and inexpensive method using programmed temperature vaporization-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (PTV-GC-MS) was developed for the simultaneous trace level determination of organometallic compounds of mercury (monomethylmercury, MMM), lead (trimethyllead, TML and triethyllead, TEL) and tin (monobutyltin, MBT; dibutyltin, DBT and tributyltin, TBT). Inorganic tin, mercury and lead species were also determined in the same chromatographic run. Prior to chromatographic separation and detection, a one-step micro liquid–liquid extraction (MLLE) after derivatization was carried out with sodium tetrapropylborate (NaBPr4) in the presence of a small volume of isooctane. Injection conditions were optimized by applying experimental designs (Plackett–Burman design (PBD) and central composite design (CCD)) using an injection volume of 25 μL. PBD was chosen to screen variables affecting the vaporization efficiency (injector heating rate, injection speed, split vent flow, injector isothermal time, injector initial temperature, oven isothermal time, oven initial temperature, and splitless time). Then, the optimum values of the significant factors (injector isothermal time, oven isothermal time and splitless time) were obtained by a CCD. The figures of merit were achieved using selective ion monitoring (SIM) and full scan modes. The instrumental detection and quantification limits were in the range of few μg L−1. Repeatability and intermediate precision in the range of 1.3–20% were achieved for most compounds studied. The accuracy of the method (average analytical recovery percentages) was satisfactory.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...