Liquid–liquid extraction and separation of lead(ii) by using N-n-octylcyclohexylamine as an extractant: analysis of real samples†
Abstract
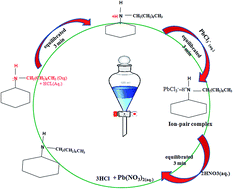
A method for the determination of micro amounts of lead(II) is described. N-n-Octylcyclohexylamine (N-n-OCA) was employed as an ion-pair forming a neutral [N-n-OCAH+PbCl3−] complex in hydrochloric acid medium. The quantitative extraction of lead(II) was observed with N-n-OCA (0.03 to 0.055 M) in a dichloromethane (DCM) and xylene mixture (1 : 4), from hydrochloric acid medium (3.0 to 5.0 M). The extracted ion-pair complex was back stripped with 0.5 M nitric acid and determined spectrophotometrically with PAR. The quantitative extraction of lead(II) was found in the DCM : xylene ratio of 1 : 4 as a mixed solvent system. The various parameters studied, such as concentration of acid, N-n-OCA concentration, equilibrium time, solvent study, back stripping agents and loading capacity were optimized for the quantitative extraction of lead(II). The stoichiometry of the extracted ion-pair complex was determined on the basis of the slope analysis method, and it was found to be 1 : 3 : 1 (metal : chloride : extractant). The proposed method was successfully applied to the analysis of diverse ions, binary mixtures of associated metal ions, ternary mixtures, alloys, ayurvedic samples and water samples, by using N-n-OCA and lead(II) was determined using PAR and the results of analysis were confirmed by ICP-OES.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...