Optimization of the procedure for efficient dispersion of titanium dioxide nanoparticles in aqueous samples
Abstract
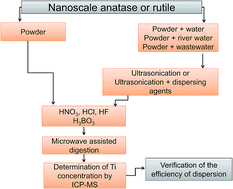
The widespread use of titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2NPs) in consumer products has led to an increase of their concentrations in the environment. For reliable determination of their total concentrations, the microwave assisted digestion procedure for the decomposition of nanoscale anatase and rutile was optimized and Ti concentrations were determined by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). To determine the TiO2NP concentration in environmental water samples, sample treatments, which maintain NPs dispersed and stabilized in solution, enabling quantitative transfer of TiO2NPs during the analytical procedure, are of crucial importance. In the present work, several dispersion approaches by the use of different mechanical and ultrasonication procedures in combination with various dispersing agents were examined in order to prepare aqueous suspensions of stable and homogeneously dispersed TiO2NPs. Experiments were performed with commercially available rutile and anatase NPs in MilliQ water. The efficiency of NP dispersion was evaluated by measuring the zeta potential and through the determination of the Ti concentration by ICP-MS after microwave assisted digestion of samples. Among different dispersion approaches, ultrasonication or ultrasonication in combination with dispersing agents, such as polyethyleneimine (PEI 600), ammonium polymethacrylate (Darvan C) or Triton X100, was found to be most effective for dispersing and stabilizing nanoscale rutile in MilliQ water. In order to verify the applicability of ultrasonication and its combination with dispersing agents, river and wastewater samples were spiked with nanoscale anatase and rutile and the stability of TiO2NP dispersions was examined by measuring the zeta potential. The results demonstrated that different environmental conditions, such as the presence of natural organic matter and ionic strength, have a significant influence on the efficiency of dispersion and the stability of TiO2NPs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...