An electrochemical biosensor for sensitive detection of Hg2+ based on exonuclease III-assisted target recycling and hybridization chain reaction amplification strategies†
Abstract
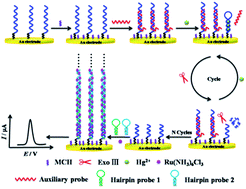
In this work, a selective electrochemical biosensor for the sensitive detection of mercury ions (Hg2+) has been developed based on the exonuclease III (Exo III)-assisted target recycling and hybridization chain reaction (HCR) amplification strategies. A thymine (T)-rich capture probe (CP) was first self-assembled on the gold electrode surface through Au–S bonding and then blocked with 6-mercaptohexanol (MCH). Subsequently, the auxiliary probe (AP) hybridized with the CP to form a double-stranded DNA (ds-DNA) structure. The presence of Hg2+ led the CP to form a T–Hg2+–T hairpin structure with recessed 3′-termini, which triggered the Exo III cleavage process accompanied by the release of Hg2+ for analyte recycling, and the remaining DNA fragments of the CP on the electrode hybridized with hairpin probe 1 (HP1) and hairpin probe 2 (HP2) to implement the HCR process. The long ds-DNA structures provided abundant adsorption sites for the electroactive complex (Ru[(NH3)6]3+), leading to a significant differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) response. The developed electrochemical biosensor afforded highly sensitive and selective detection of Hg2+, and the analytical method would have great potential applications in the monitoring of Hg2+ in real environmental samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...