Development and validation of a reversed phase liquid chromatographic method with fluorescence detection for the pharmacokinetic study of a new chimeric peptide
Abstract
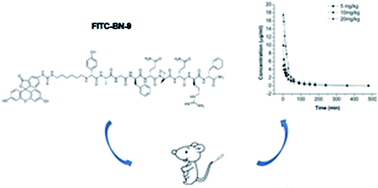
The objective of this research is to develop a sensitive bioanalytical method and investigate the pharmacokinetics of a new chimeric peptide (BN-9) in rats. According to the analysis criteria, a reversed phase high performance liquid chromatography method with fluorescence detection (HPLC-FLD) was established and employed in monitoring the compound in rat plasma using doxorubicin (DOX) as the internal standard (IS). Fluorescent BN-9 and IS were extracted from plasma using dehydrated alcohol. The mobile phase was composed of acetonitrile and potassium dihydrogen phosphate buffer containing 0.05% trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) (pH 7.4; 0.02 M) (30 : 70, v/v) at 0.7 mL min−1. Fluorescence detection was conducted at 490 nm (excitation wavelength) and 520 nm (emission wavelength). The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) was 0.009 µg mL−1. The intra-batch and inter-batch precisions were less than 8.116%, and the accuracy was within 5.632%. Blood samples were collected after intravenous administration of fluorescent BN-9 at the doses of 5, 10, and 20 mg kg−1 to rats. The main pharmacokinetic parameters were obtained by non-compartmental and compartmental analysis with DAS 2.1.1 software. The t1/2α values were 9.584 ± 5.137, 8.548 ± 2.093 and 9.621 ± 0.3224 min. The results showed that the method was successfully applied to investigate the pharmacokinetic profiles of fluorescent BN-9 following intravenous administration to rats.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...