A strategy for quality control of the fruits of Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt based on antioxidant activity and fingerprint analysis
Abstract
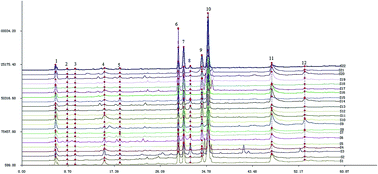
Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt is widely used as an edible and medicinal plant in Asian countries, and its fruits have been adopted in Chinese pharmacopoeia as a traditional Chinese medicine (TCM). To provide an efficient method for quality control, an attempt to explore antioxidant activity and fingerprint analysis was made in this work. 1,1-Diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl radical (DPPH) scavenging activities of the fruits of P. frutescens from different sources were measured first. Then, HPLC fingerprints of these samples were established and four active components were deduced by multiple correlation analysis. Combined with TLC bioautography assay and HPLC comparison, the four antioxidant components separated by silica gel chromatography and further purified by Sephadex LH-20 were determined to be caffeic acid, rosmarinic acid, luteolin and apigenin, respectively. Finally, total phenolic contents of the test samples were determined and their correlation with antioxidant activity was also investigated. The results indicated that most of the similarities of 22 batches of samples were more than 0.89 based on the four active components corresponding to the peaks 5, 10, 11 and 12 in the fingerprints and total phenolic contents correlated closely with antioxidant activity. Therefore the four components and total phenols are predominant contributors to the antioxidant activity of the fruits of P. frutescens. It is proposed that the fingerprint with the four characteristic peaks as common peaks and total phenolic content determination were necessary for the quality control of this plant and should be adopted in its quality standards.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...