Automated analysis of food-borne pathogens using a novel microbial cell culture, sensing and classification system†
Abstract
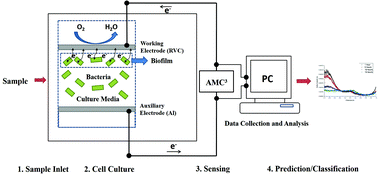
We hereby report the design and implementation of an Autonomous Microbial Cell Culture and Classification (AMC3) system for rapid detection of food pathogens. Traditional food testing methods require multistep procedures and long incubation period, and are thus prone to human error. AMC3 introduces a “one click approach” to the detection and classification of pathogenic bacteria. Once the cultured materials are prepared, all operations are automatic. AMC3 is an integrated sensor array platform in a microbial fuel cell system composed of a multi-potentiostat, an automated data collection system (Python program, Yocto Maxi-coupler electromechanical relay module) and a powerful classification program. The classification scheme consists of Probabilistic Neural Network (PNN), Support Vector Machines (SVM) and General Regression Neural Network (GRNN) oracle-based system. Differential Pulse Voltammetry (DPV) is performed on standard samples or unknown samples. Then, using preset feature extractions and quality control, accepted data are analyzed by the intelligent classification system. In a typical use, thirty-two extracted features were analyzed to correctly classify the following pathogens: Escherichia coli ATCC#25922, Escherichia coli ATCC#11775, and Staphylococcus epidermidis ATCC#12228. 85.4% accuracy range was recorded for unknown samples, and within a shorter time period than the industry standard of 24 hours.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...