A highly sensitive strategy for base excision repair enzyme activity detection based on graphene oxide mediated fluorescence quenching and hybridization chain reaction†
Abstract
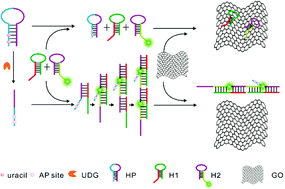
A novel fluorescent nanosensor has been developed by combining super fluorescence quenching ability of graphene oxide and hybridization chain reaction amplification, which enables highly sensitive detection of base excision repair enzyme activity with a wide dynamic range from 0.0001 to 100 U mL−1 and a detection limit of 0.00006 U mL−1.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...