Synthesis and optical nonlinear properties of novel Y-shaped chromophores with excellent electro-optic activity
Abstract
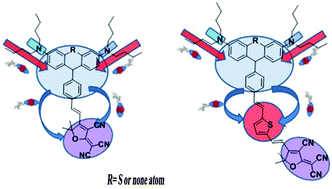
A series of Y-shaped chromophores A1, A2, B1 and B2 based on the same thiophene π-conjugation and tricyanofuran acceptor (TCF) but with different donors (modified phenothiazine and triphenylamine) have been synthesized and systematically investigated in this paper. Density functional theory (DFT) was used to calculate the HOMO–LUMO energy gaps and first-order hyperpolarizability (β) of these chromophores. These chromophores showed excellent thermal stability with their decomposition temperatures all above 270 °C. Most importantly, the high molecular hyperpolarizability of these chromophores can be effectively translated into large electro-optic (EO) coefficients (r33) in poled polymers. The doped film-C containing 25 wt% chromophore B1 displayed an r33 value of 72 pm V−1 at 1310 nm, and the doped film-D containing B2 showed a value of 95 pm V−1 at a concentration of 25 wt%. These values are all much higher than the traditional FTC chromophore (39 pm V−1). High r33 values indicated that the special Y structure can reduce intermolecular electrostatic interactions and thus enhance the macroscopic EO activity. These properties, together with the good solubility, suggest the potential use of these new chromophores as materials for advanced devices.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...