Synthesis and super-resolution imaging performance of a refractive-index-controllable microsphere superlens†
Abstract
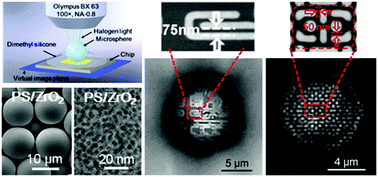
Microspheres can function as optical superlenses for nanoscale super-resolution imaging. The imaging performance is mainly affected by the size and refractive index of the microsphere. Precise control of these parameters is a challenging task but of fundamental importance to the further development of the technique. In this study, we demonstrate for the first time a nanoparticle-hybrid suspension polymerization approach to chemically synthesize high-quality microspheres (ZrO2/polystyrene) with optical properties that are highly controllable. Microspheres of different sizes (d: 2–20 μm) and refractive indexes (np: 1.590–1.685) were synthesized and their super-resolution imaging performances were evaluated and compared. Our results show that continuously increasing the refractive index of microspheres can enhance the imaging resolution and quality. A 60 nm resolution has been obtained in the wide-field imaging mode and a 50 nm resolution has been obtained in the confocal mode imaging of semiconductor chip samples. The obtained 50–60 nm resolutions have significantly gone beyond the conventional 200 nm resolution limit for visible light optical microscopes; the super-resolution mechanism has been discussed. The synthesized microsphere superlenses may find applications in many other areas as well, including nanolithography, nano-sensing, nano-diagnosis, nano-spectroscopy and ultra-high density optical data storage.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...