Soluble fluorescent polymeric nanoparticles based on pyrrole derivatives: synthesis, characterization and their structure dependent sensing properties†
Abstract
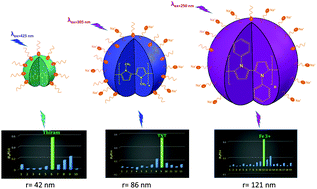
The electrostatic stabilization concept based on an anionic surfactant, dodecylbenzenesulfonate (DBS−), was applied to prepare soluble and fluorescent polypyrrole (PPy) nanoparticles. The effect of N-substitution as well as synthesis conditions, i.e. the surfactant to monomer mole ratio and oxidant addition type (one-step or multi-step), on the size, molecular weight, structure and spectroscopic properties of polymer nanoparticles was evaluated. PPy nanoparticles synthesized at a surfactant to monomer mole ratio of 0.20 : 1 and five-step addition of an oxidant show the most intense fluorescence, narrowest particle size and lowest molecular weight. FT-IR, UV-vis, XPS and ICP-OES confirmed that surfactant molecules are incorporated into the polymer structures. The synthesized polymer nanoparticles were classified into two categories based on their conductivities in solution phase and ICP-OES measurements: indissociable polymer nanoparticles (PPy) which contain only anion dopant surfactants and dissociable polymer nanoparticles, poly N-methyl pyrrole (NmPPy) and poly N-phenyl pyrrole (NphPPy), which contain anion dopants and hydrophobically attached surfactant molecules. The experimental results of conductometry, XPS, ICP-OES and GPC were combined to propose polymer unit structures for all the synthesized polymer nanoparticles. UV-vis and fluorescence measurements in different solvents were used to gain insight into the dipole moments of the excited and ground states of polymer nanoparticles. Finally, the potential application of the polymer nanoparticles in fluorescence sensors was investigated by recording their response to various chemical species and it was found that the polymer nanoparticles have structure dependent sensing behaviors. PPy and NmPPy nanoparticles show the most sensitive response to C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) S containing and nitro-aromatic compounds, respectively, while NphPPy nanoparticles exhibit a selective and profound response to Fe3+ ions. The results of this work will benefit scientists who are working on the synthesis and basic studies of soluble polymer materials and the design of advanced fluorescence sensors.
S containing and nitro-aromatic compounds, respectively, while NphPPy nanoparticles exhibit a selective and profound response to Fe3+ ions. The results of this work will benefit scientists who are working on the synthesis and basic studies of soluble polymer materials and the design of advanced fluorescence sensors.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...