High efficiency blue fluorescent organic light-emitting diodes using a conventional blue fluorescent emitter
Abstract
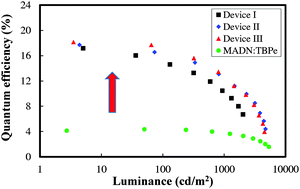
High efficiency blue fluorescent organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) were developed by doping the conventional 2,5,8,11-tetra-tert-butylperylene (TBPe) blue fluorescent dopant in a mixed emitting layer of a wide bandgap host and a blue thermally activated delayed fluorescent emitter which played the role of a sensitizer in blue fluorescence emission. 10-(4-((4-(9H-Carbazol-9-yl)phenyl)sulfonyl)phenyl)-9,9-dimethyl-9,10-dihydroacridine (CzAcSF) was the blue thermally activated delayed fluorescent emitter of the emitting layer and bis[2-(diphenylphosphino)phenyl]ether oxide (DPEPO) was the host material of the emitting layer. Doping of TBPe at a doping concentration of 0.1% in an emitting layer of DPEPO:CzAcSF achieved a high quantum efficiency of 18.1% in the blue fluorescent OLEDs, which is the best quantum efficiency reported in blue fluorescent OLEDs.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...