Silica-encapsulated semiconductor polymer dots as stable phosphors for white light-emitting diodes
Abstract
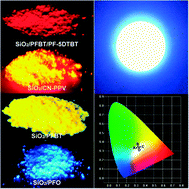
Semiconductor polymer dots (Pdots) were encapsulated into a SiO2 matrix to form fluorescent nanocomposites using a modified Stöber method. Significantly, the photostability and thermal stability of the nanocomposites were greatly improved as compared to those of pure Pdots. The luminescent nanocomposites combined with blue LEDs result in white-light emitting devices with a high color-rendering index.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...